Osteocartilage degeneration is called a dispersive deep disease of vertebral osteocartilage tissue, causing their destruction.Osteochondrosis is located in the vertebrae of the thoracic vertebrae called sternum osteochondrosis.Compared with other localized osteochondria - cervical or lumbar spine - chest osteochondria is rarely diagnosed with anatomical features of the chest structure.This is a relatively static structure in which the spine itself has relatively small mobility, respectively - even pathological processes that are active in the intervertebral disc, the possibility of damage is small.In the recent past, sternum osteocartilage has been considered a privilege for specialized elderly patients when diagnostic capabilities are limited.Now, it can be identified not only in young people, but even in childhood.

Why does sternum chondrochondrosis develop?
Among the causes of sternum osteochondrosis, the following contents should be distinguished:
- Pathology of vertebrae and intervertebral discs - inherited and acquired pathology due to various factors;
- Blood supply that invades the spine blood;
- Excessive or irrational physical exercise on the spine (when exercising or due to hard physical work);
- Violating the body's mineral metabolism, the lack of some trace elements;
- A sedentary lifestyle, a professional sedentary activity;
- Weakness in the back muscles leads to improper loading on the spine;
- Injuried.
In addition, there are many factors that can intensify the chronic course of the disease:
- Injuried;
- stress, over-tension;
- Hypothermia in the body - general and local hypothermia in the back muscles;
- Excessive physical fatigue.
Why is sternum and cartilage disease dangerous?
Osteocartilage degeneration in the thoracic spine is a disease accompanied by significant pathological changes in the vertebrae and vertebrae joints.Therefore, the first result of this disease is to destroy the structure that forms the spine.This may be a result of scoliosis, pathology of the respiratory system (pneumonia, pneumonia), impaired blood circulation in internal organs, upper gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, cholecystitis).The negative consequences of sternum osteochondrosis can also be applied to the curriculum system.Characteristics of osteochondrosis: Persistent pain syndrome, which reduces the quality of life and can "camouflage" other diseases, which can lead to improper diagnosis and treatment.
How does sternum chondrochondrosis manifest?
With sternum osteochondrosis, the symptoms are very characteristic:
- pain- This happens when a person is in a position for a long time and when exercising, lifting weights, and physically working hard.Dull and persistent pain in the shoulder blob area is characteristic and painful when trying to raise your hand;
- Intercostal neuralgia;
- Feelings on the chestTherefore, deep breathing becomes difficult;
- Reduced sensitivitySome areas of the skin;
- abnormal- The feeling of "crawling chicken skin" on the skin, burning, stinging;
- Temperature reductioncertain areas on the skin;
- Temperature reductionLeg skin,The feeling of itching BurningIn them
- Digestive disorders.
There are two basic types of pain types in the thoracic spine: dorsal algiyu (prolonged pain in spinal cartilage) and dorsago (strong paroxysmal pain accompanied by strong paroxysmal pain with muscle spasms and dyspnea).
Osteochondrosis known as So is a characteristic of osteochondrosisGastric syndrome- Epithelial pain has nothing to do with daily life or time of year.
Severity of sternum chondrochondrosis
In clinical practice, the 4 degrees of thoracic vertebrae are distinguished based on the degree of damage to the cartilage and the degree of damage involved in the pathological processes surrounding the surrounding structure.
Sternum osteochondral disease in the first grade of spine:The disc between the vertebrae loses elasticity, some become thinner, and locally protrudes - the protrusion may appear in the fibrous annulus of the disc.
Secondary degree of sternum osteocartilage:Thinning of the intervertebral disc is underway and the thoracic spine has lost its stability.At this stage, pain begins to bother, and usually neurological symptoms are added: abnormal sensation and numbness of the skin.Cracks may appear on the annulus of the intervertebral disc.
Sternum bone and cartilage of the spine 3 degreesCorresponding to the formation of vertebral hernia.
Sternum chondrochondrosis 4 degreesIt is characterized by its depreciation characteristics of complete loss of vertebrate discs.The binding of the vertebrae becomes critical and the bone tissue begins to collapse.In the canals of the spine, blood vessels and nerves are violated, leading to persistent neurological symptoms, strengthening Bolevomu syndrome, and circulatory disease.
Diagnosis of sternum and cartilage disease
Based on the investigation, examination and examination of patients: radiograph and magnetic resonance imaging, the diagnosis of "chest osteochondral disease" was diagnosed.An X-ray study helps determine the localization of spinal lesions, while magnetic resonance imaging is an elucidation of the diagnosis to rule out the presence of benign and malignant tumors.
Many symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are nonspecific – the same signs may indicate other diseases.This explains frequent errors in the diagnosis, such as the patient treats pancreatitis for a prolonged period of time due to pain, which is the real cause, and the real cause is osteocartilage of the breast.Therefore, it is important to have a comprehensive diagnosis that attracts neighboring experts - gastroenterologists, pulmonologists - to perform additional examinations on patients.
Sternum osteochondrosis: Treatment
Given that it is impossible to recover damaged cartilage, it is possible to effectively treat osteochondrosis in the breast only in the initial stages of the disease until the cartilage has not lost its structure.Therefore, it is especially important to consult a doctor in time - when the first manifestation of pathology, back discomfort, insignificant pain, numbness in the skin area, or its burning sensation occurs.
In the first stage of the disease, treatment comes down to taking non-nucleic acid analgesics, which allow pain and non-sclerotic anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process in the tissue and eliminate pain.However, the main focus of the initial stage of thoracic osteochondrosis is the reception of epinephrine.This is the name of a group of drugs designed to restore normal metabolism in cartilage tissues, which improves the slowdown of cartilage nourishment and destruction.
As the pathological process of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs progresses, inflammation can be relieved, and often it becomes insufficient, which forces doctors to supplement Cortico's glucose with steroid drugs.Additionally, diuretics can be added to the list of medications that can eliminate swelling invading the spinal nerve roots, thereby alleviating appropriate neurological symptoms and pain.Incorporating anti-spasm drugs into treatment can eliminate muscle spasms, which are accompanied by osteochondral vertebrae.
With the development of vertebral hernia and the destruction of vertebral bone tissue, conservative treatment has lost its effectiveness, and the only reasonable option is surgical treatment of osteocartilage bone.
Physical therapy for breast osteocartilage
Outside of the worsening period, physical therapy has brought good results.Effective methods for thoracic osteochondrosis include:
- laser therapy;
- Magnetic therapy;
- Extension - dry and wet;
- vacuum therapy;
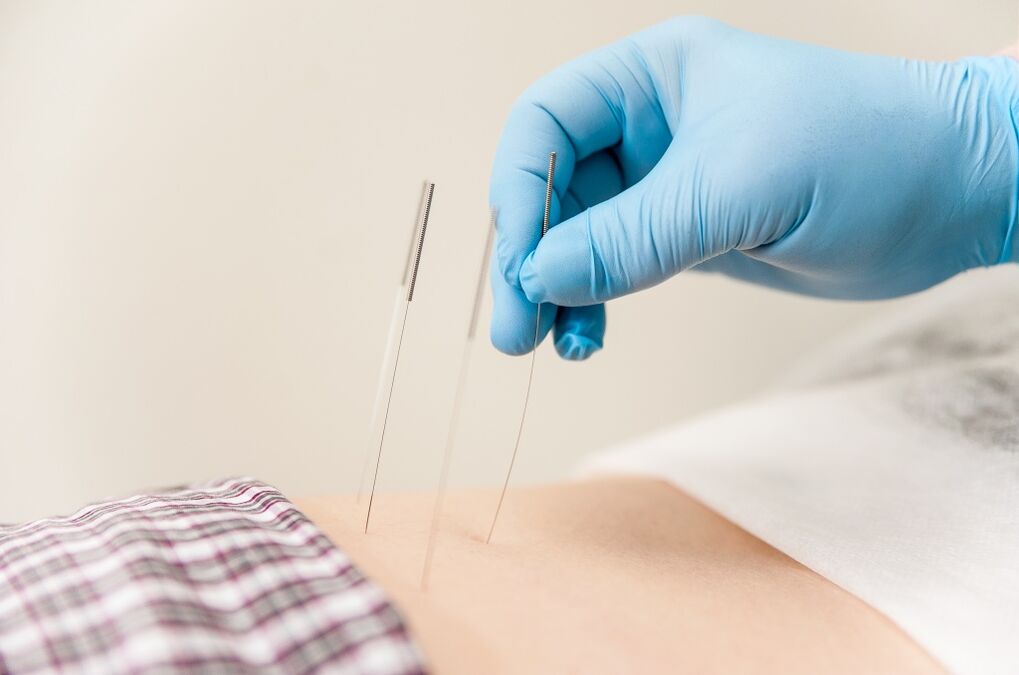
- acupuncture;
- Farmakopunktura.
In addition, massage and manual therapy include popular and effective physical therapy methods that can be used for osteochondrosis of the breast.Preventive massage classes for patients with osteochondrosis in the chest area are performed at least twice a year.At the same time, any operation should be as few as possible, only outside the aggravation period, so as not to intensify the pathological process.

Media Sports for Chest Osteochondrosis
An important part of the complex treatment of osteochondrosis in the spine and chest is the treatment of physical fitness (exercise therapy).The task of exercise is to restore the mobility of vertebrae joints, eliminate muscle spasms, and eliminate spinal stiffness.LFK allows you to strengthen your muscle corset and increase your body mobility throughout your patient, an important factor in blood circulation stimulation and restoring lung ventilation.
You should do a slightly general warmth before doing a complex with special exercises – designed to warm your muscles or take a warm shower.High-quality heating before class avoids injuries.All movements should be smooth and it is necessary to avoid sharp tendencies and turns, thereby aggravating the damage to the spine.
Osteochondrosis in the chest and spine is a chronic disease that significantly reduces the quality of the patient's life, which is a danger of his complications.Timely targeting doctors and qualified complex treatments, starting with the first sign of the disease, will help stop the pathological process and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.



































